11.gif) image by Fred Drews, 21
March 2020
image by Fred Drews, 21
March 2020
Last modified: 2020-04-19 by rob raeside
Keywords: alajuela | san carlos |
Links: FOTW homepage |
search |
disclaimer and copyright |
write us |
mirrors
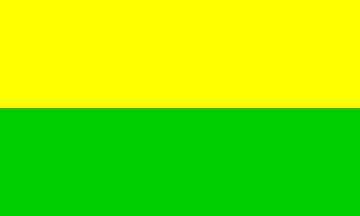 image by Ivan Sache, 22 July 2014
image by Ivan Sache, 22 July 2014See also:
The municipality of San Carlos (33,730 ha), forming Canton No. 10 of the
Alajuela Province, is the biggest canton of Costa Rica by its area; it
represents 6.5% of the national area and 2/3 of the provincial area. The canton
is divided into 14 districts: Ciudad Quesada, Florencia, Buena Vista, and Aguas
Zarcas (est. in 1911 by Decree No. 117), Venecia (est. in 1935 by Decree No.
100), Pital (est. in 1948 by Decree No. 38), Fortuna, Tigra, and Palmera (est.
in 1952 by Decree No. 15), Venado (est. in 1970), Cutris (est. in 1971 by Decree
No. 2,083), Monterrey (est. in 1979), and Pocosol (est. in 1983 by Decree No.
231).
San Carlos is named for fort San Carlos de Austria, erected in 1667
by the Spaniards on the bank of river San Juan. The fort, named for King Charles
II, was established by the Guatemala Real Audience to protect the provinces of
Nicaragua and Costa Rica from the pirates' raids. Funded for 12,000 pesos by the
Real Audiencia and the Vice-Roy of Peru, the building of the fortress was
assigned to Captain Juan Fernández Salinas de la Cerda, from Toledo, a Knight of
the Order of Calatrava who served as Governor of Costa Rica from 1650 to 1659.
Originally located moved at the mouth of river Pocosol / Cutris, the site of the
fort was eventually moved to the northern bank of River San Juan, closer to the
island that faced the mouth of Pocosol. While commissioned to establish a strong
and safe fortress, the captain indeed erected a small fort protected by posts
and an earthen wall. On the other side of the river, he established a fortified
camp named San Juan de Dios, which was connected to the castle by a cable
equipped with a lantern lighting the river. The captain was eventually tried in
Santiago de los Caballeros de Guatemala for his lack of care and disobedience.
The loose fortifications were destroyed in 1670 by the pirate Gallardillo,
with the cooperation of Captain Gonzalo Noguera, commander of the garrison. The
pirates then sacked the town of Granada, for the second time within 15 years.
This event prompted the Spanish authority to establish safer fortifications.
Fort Inmaculada Concepción, known today as Castillo Viejo (Old Fort) was built
in 1675 close to the Santa Cruz waterfall. Another fort was subsequently
established near the source of river San Juan. River Pocosol / Cutris was
renamed river San Carlos by the Spaniards; this name was progressively given to
the whole territory watered by the river and its tributaries.
Francisco
Martínez established in 1850 a trail through the then uninhabited territory of
San Carlos; however, the first permanent settler in the area was Victoriano
Fernández Carrillo, who settled there in 1851. The old San Carlos trail was used
in 1856-1857 by the national army fighting against William Walker. Colonization
increased in 1851-1883, with 67 plots conceded to national and foreign owners;
most of them, however, did not live on the conceded territories. Joaquín Quesada
founded in 1890-1891 the settlement of La Unión, on a plot belonging to José
María Quesada Ugalde. The Aguas Zarcas colony was established in 1893 by Decree
No. 31. The canton of San Carlos was established in 1911 by Decree No. 17; the
municipality was inaugurated in 1914. Zapote, Lajas and Santa Elena seceded from
San Carlos in 1939, by Decree No. 35. In 1950, the villagers of La Tigra and La
Fortuna decided in a plebiscite to join San Carlos; this was the first time
women were allowed to vote in Costa Rica. Villa Quesada was granted the title of
"ciudad" in 1953 by Law No. 1,601. In 1968, an eruption of volcano Arenal
suppressed the villages of Pueblo Nuevo and Tabacón, claiming 67 lives.
http://www.munisc.go.cr - Canton's website
The flag of San Carlos is horizontally divided yellow-green. Yellow is the
colour of the flowers of the canton's official tree, the yellow guayacan. Green
represents the abundant flora of the canton.
http://www.munisc.go.cr/Paginas/Visitantes/SimbolosCanton.aspx - Municipal
website
The yellow guayacan [Tabebuia guayacan (Seem.) Hemsl.,
family Bignoniaceae], locally known as "corteza amarillo" (Spanish, yellow
bark), was proclaimed the canton's tree by Act No. 91 of 17 September 1996. It
is found from Mexico to Colombia, mostly on the Atlantic coast. It is considered
as an endangered species in Costa Rica.
http://darnis.inbio.ac.cr/FMPro?-DB=UBIpub.fp3&-lay=WebAll&-Format=/ubi/detail.html&-Op=bw&id=2138&-Find
Ivan Sache, 22 July 2014
11.gif) image by Fred Drews, 21
March 2020
image by Fred Drews, 21
March 2020
a-11.gif) image contributed by Fred Drews, 23 March 2006
image contributed by Fred Drews, 23 March 2006